Understanding Three-Bedroom Duplex Plans

A three-bedroom duplex offers a practical and versatile living solution for families, individuals, or investors seeking a balance between space and affordability. This type of dwelling provides separate living units, typically with two floors, each featuring three bedrooms, a kitchen, a living room, and bathrooms. Understanding the different types of three-bedroom duplex plans and their features can help you choose the ideal option for your needs.
Types of Three-Bedroom Duplex Plans
The layout of a three-bedroom duplex can vary significantly depending on its design and the arrangement of the living units. Here are the most common types:
Side-by-Side Duplex
This configuration features two identical units placed side by side, sharing a common wall. Each unit has its own entrance, backyard, and separate utilities. This type is often preferred for its privacy and independent living spaces.
Advantages:
- Privacy: Each unit enjoys its own entrance and backyard, ensuring privacy for residents.
- Independent living: Residents have complete control over their living space and utilities.
- Potential for rental income: Owners can rent out one or both units for passive income.
Disadvantages:
- Limited shared space: Residents have minimal shared space, which may limit social interaction.
- Higher construction costs: Building two separate units can be more expensive than a stacked duplex.
Example:
A typical side-by-side duplex might feature two identical units with a living room, dining room, kitchen, three bedrooms, and two bathrooms each. The units would share a common wall, with each unit having its own entrance, backyard, and parking space.
Stacked Duplex
In this configuration, two units are stacked vertically, with one unit occupying the upper floor and the other the lower floor. They typically share a common entrance and some utilities.
Advantages:
- Smaller footprint: Requires less land than a side-by-side duplex, making it suitable for smaller lots.
- Lower construction costs: Building a stacked duplex can be more cost-effective than a side-by-side duplex.
- Potential for shared amenities: Residents can enjoy shared amenities such as a common laundry room or backyard.
Disadvantages:
- Less privacy: Residents may experience less privacy due to shared entrances and utilities.
- Noise concerns: Noise from the upper unit can be a concern for residents on the lower floor.
Example:
A stacked duplex could feature a lower unit with a living room, dining room, kitchen, three bedrooms, and two bathrooms, while the upper unit might have a similar layout with a separate entrance and shared laundry facilities.
Attached Duplex
Attached duplexes are similar to side-by-side duplexes but with a shared wall extending beyond the living area. This configuration offers a more connected living experience with potential for shared outdoor spaces.
Advantages:
- Shared outdoor space: Residents can enjoy shared amenities such as a common patio or backyard.
- Potential for social interaction: Residents have opportunities for interaction and community building.
Disadvantages:
- Less privacy: Residents may experience less privacy due to shared walls and outdoor spaces.
- Potential for conflicts: Shared amenities can lead to potential conflicts between residents.
Example:
An attached duplex could feature two units with a shared wall extending to a common patio and backyard. Each unit would have its own entrance, living room, dining room, kitchen, three bedrooms, and two bathrooms.
Benefits of a Three-Bedroom Duplex
Three-bedroom duplexes offer several advantages for families, individuals, and investors:
For Families:
- Spacious living: Provides ample space for families with children, offering separate bedrooms and living areas.
- Affordable housing: Duplexes can be more affordable than single-family homes, making them a viable option for families with a budget.
- Community living: Duplexes often foster a sense of community, allowing families to interact with neighbors.
For Individuals:
- Privacy and independence: Offers a private living space with separate entrances and utilities.
- Lower maintenance costs: Sharing common areas and utilities can reduce individual maintenance costs.
- Potential for rental income: Owners can rent out the other unit for passive income.
For Investors:
- High rental demand: Three-bedroom duplexes are in high demand, providing potential for steady rental income.
- Appreciation potential: Duplexes tend to appreciate in value over time, providing long-term investment returns.
- Tax benefits: Investors can deduct expenses related to the property, such as mortgage interest and property taxes.
Design Considerations for Three-Bedroom Duplexes: Three Bedroom Duplex Plan
Creating a well-designed three-bedroom duplex requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure both functionality and aesthetics. From optimizing space to prioritizing accessibility, each element plays a crucial role in the overall success of the project.
Optimizing Space for Different Areas
Effective space utilization is paramount in duplex design, particularly for three-bedroom units. Here are some key considerations:
- Bedrooms: Ensure sufficient space for comfortable sleeping arrangements, furniture placement, and adequate closet space. Consider incorporating built-in storage solutions to maximize space and minimize clutter.
- Living Areas: Design spacious and inviting living rooms that accommodate comfortable seating, entertainment systems, and potential dining areas. Consider open-plan layouts to create a sense of flow and maximize natural light.
- Kitchens: Plan for efficient kitchen layouts with ample counter space, storage, and appliances. Consider using compact appliances, maximizing vertical space, and incorporating island layouts for added functionality.
- Bathrooms: Design functional bathrooms with sufficient space for a shower or bathtub, toilet, vanity, and storage. Consider using space-saving fixtures and incorporating mirrors to create an illusion of greater space.
Creating Balanced Flow and Separation Between Units, Three bedroom duplex plan
Maintaining a balance between privacy and shared spaces is crucial for successful duplex design. Here are some tips:
- Entryways: Design separate entryways for each unit, providing a sense of privacy and individual access.
- Soundproofing: Implement effective soundproofing measures between units, such as using thicker walls, sound-absorbing materials, and strategically placed doors.
- Shared Spaces: Consider including shared amenities, such as a laundry room or outdoor space, to foster a sense of community while maintaining privacy.
Incorporating Natural Light and Ventilation
Maximizing natural light and ventilation is essential for creating comfortable and energy-efficient living spaces.
- Windows: Strategically place windows to allow ample natural light and ventilation throughout the units. Consider using large windows or skylights to maximize light penetration.
- Cross-Ventilation: Design units with cross-ventilation, allowing air to flow freely through the space. This helps to maintain a comfortable temperature and reduce reliance on air conditioning.
- Outdoor Spaces: Incorporate balconies, patios, or courtyards to provide residents with access to fresh air and natural light.
Designing for Accessibility and Safety
Creating accessible and safe living spaces is essential for all residents. Consider these factors:
- Entryways: Design entryways with ramps or wide doorways to accommodate wheelchair users or those with mobility challenges.
- Bathrooms: Include grab bars, non-slip flooring, and accessible shower stalls for enhanced safety and accessibility.
- Lighting: Provide adequate lighting throughout the units, particularly in stairwells and hallways, to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
- Fire Safety: Implement fire safety features such as smoke detectors, fire extinguishers, and fire-resistant materials to comply with local building codes and ensure the safety of residents.
Maximizing Space in Each Unit
Efficient space planning is crucial for creating functional and comfortable three-bedroom duplex units. Here are some tips for maximizing space:
- Built-in Storage: Incorporate built-in storage solutions, such as closets, shelves, and cabinets, to maximize space and minimize clutter.
- Multi-Functional Furniture: Use multi-functional furniture, such as sofa beds or dining tables with storage, to optimize space and provide flexibility.
- Vertical Space: Maximize vertical space by utilizing shelves, wall-mounted storage units, and high cabinets.
- Mirrors: Strategically placed mirrors can create an illusion of greater space by reflecting light and expanding the visual field.
Considering Local Building Codes and Regulations
Compliance with local building codes and regulations is essential for ensuring the safety and legality of the duplex project.
- Zoning Regulations: Understand local zoning regulations regarding the number of units allowed, setbacks, and other requirements.
- Building Codes: Adhere to building codes related to structural integrity, fire safety, electrical wiring, plumbing, and other essential aspects of construction.
- Accessibility Standards: Ensure compliance with accessibility standards for entryways, bathrooms, and other areas to create inclusive living spaces.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Meet local energy efficiency standards for insulation, windows, and appliances to promote sustainability and reduce energy consumption.
Building a Three-Bedroom Duplex
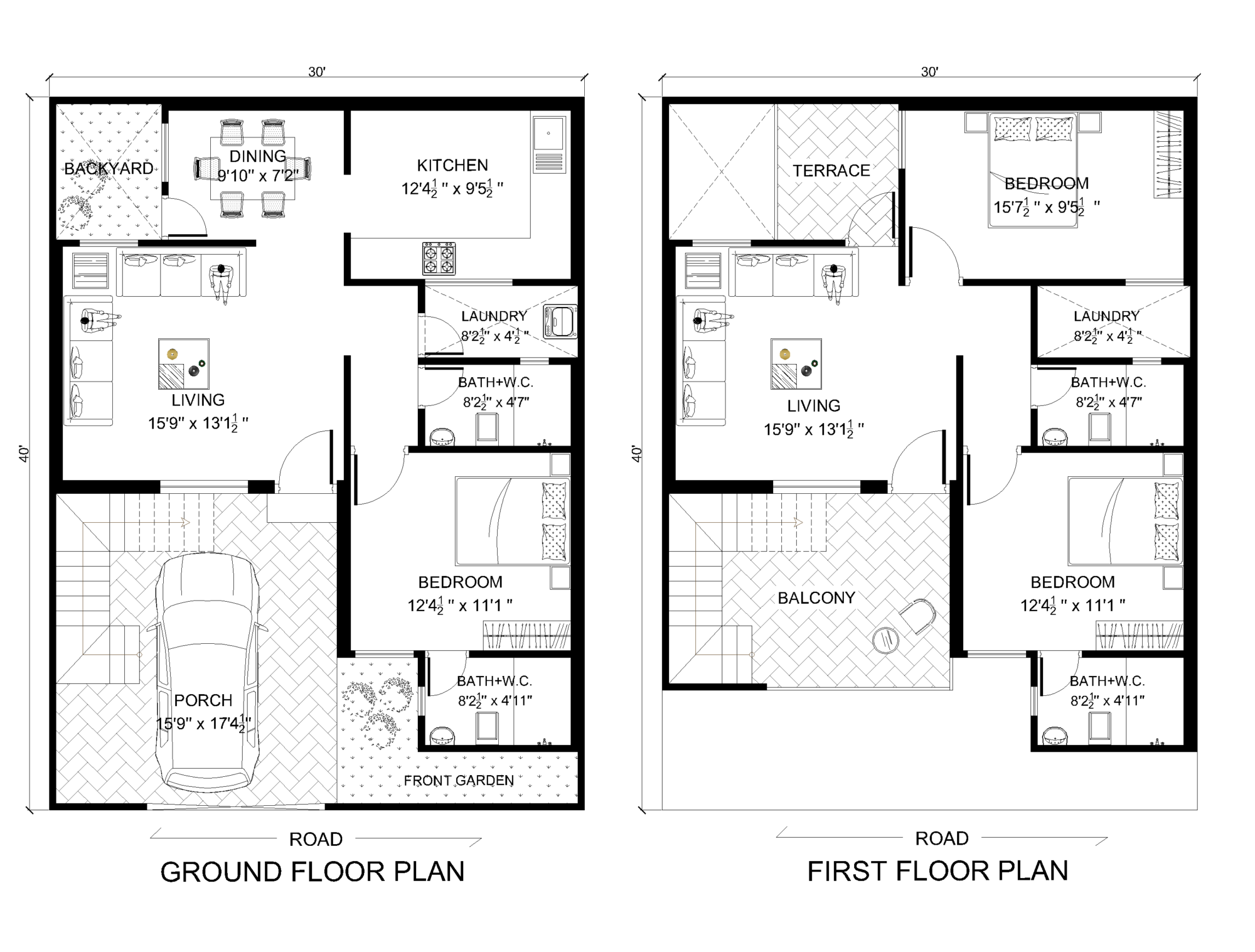
Building a three-bedroom duplex is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning, execution, and financial management. From conceptualization to completion, the process involves a series of steps, each with its own set of considerations. Understanding these steps and the associated challenges is crucial for a successful project.
Planning and Design
The initial phase involves defining the project scope, developing the design, and obtaining necessary permits. This phase lays the foundation for the entire construction process.
- Defining the Project Scope: This involves determining the specific features of the duplex, such as the number of bedrooms and bathrooms, the size and layout of the units, and the desired level of finishes.
- Developing the Design: This involves creating detailed plans and specifications for the duplex, including architectural drawings, structural plans, and electrical and plumbing layouts.
- Obtaining Permits: This involves securing necessary permits from local authorities, such as building permits, zoning permits, and utility permits.
Construction
The construction phase involves the actual building of the duplex, from laying the foundation to installing the finishing touches. This phase requires skilled labor and careful coordination.
- Foundation: The foundation is the base of the duplex, providing structural support. Common foundation types include concrete slabs, crawl spaces, and basements. The choice of foundation depends on factors such as soil conditions and local building codes.
- Framing: The framing provides the structure for the walls, roof, and floors. Common framing materials include wood, steel, and concrete.
- Roofing: The roof protects the duplex from the elements. Common roofing materials include asphalt shingles, metal, and tile.
- Exterior Finishes: Exterior finishes include siding, windows, doors, and landscaping. These elements contribute to the aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency of the duplex.
- Interior Finishes: Interior finishes include drywall, flooring, cabinets, and fixtures. These elements create the living spaces within the duplex.
Materials and Construction Methods
The choice of materials and construction methods can significantly impact the cost, durability, and energy efficiency of the duplex.
- Building Materials: Common building materials include wood, concrete, steel, brick, and stone. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, durability, and environmental impact.
- Construction Methods: There are various construction methods available, such as traditional stick-built construction, modular construction, and prefabricated construction. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, speed, and quality.
Financial Considerations
Building a duplex involves significant financial investment. Careful budgeting and financing are essential for a successful project.
- Budgeting: Developing a realistic budget is crucial. This involves estimating the cost of land, materials, labor, permits, and other expenses.
- Financing Options: There are various financing options available, including construction loans, mortgages, and private financing. The choice of financing depends on factors such as credit score, down payment, and loan terms.
- Return on Investment: The potential return on investment depends on factors such as rental income, operating expenses, and property appreciation. It is important to conduct thorough market research and financial analysis to estimate the potential return on investment.
